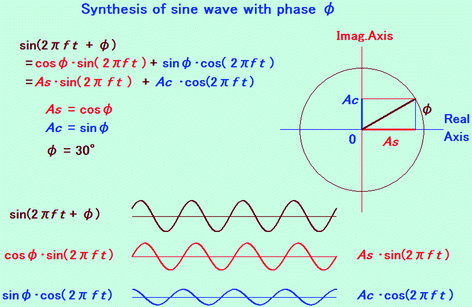
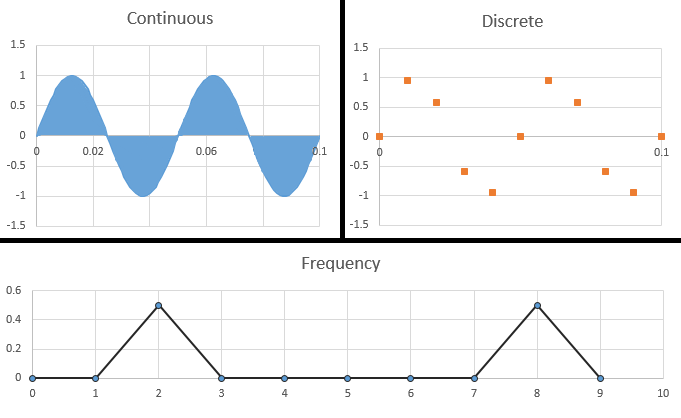
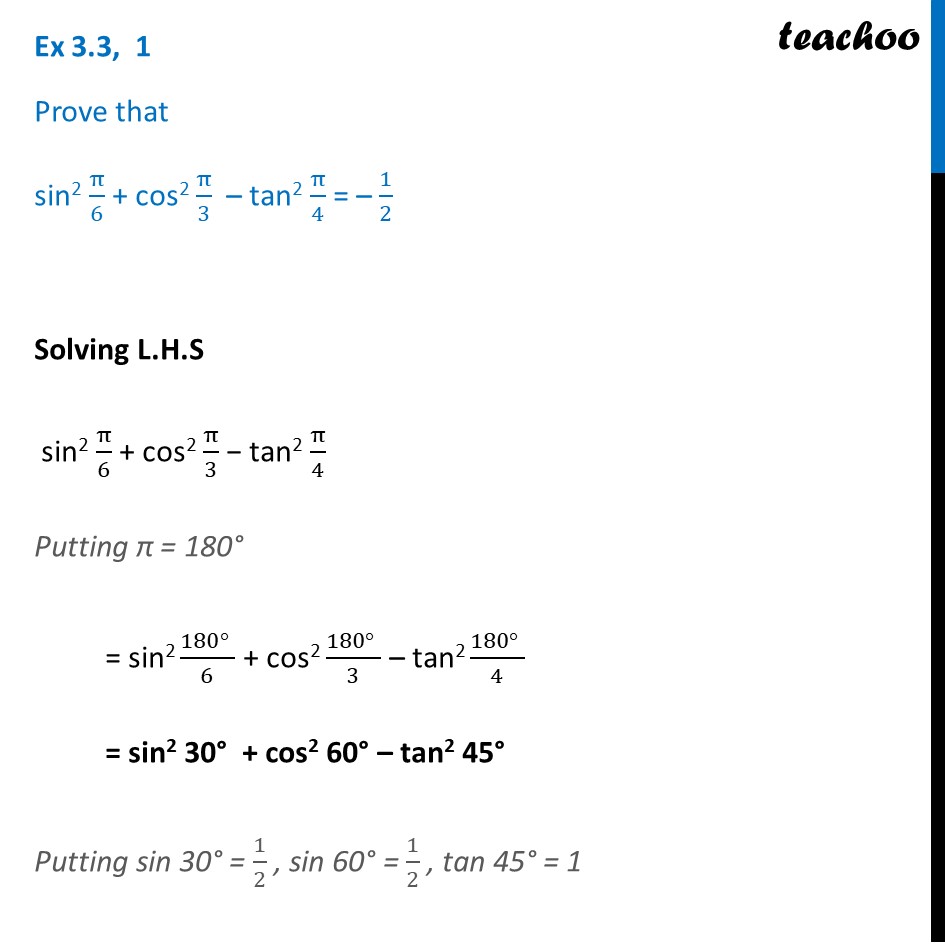
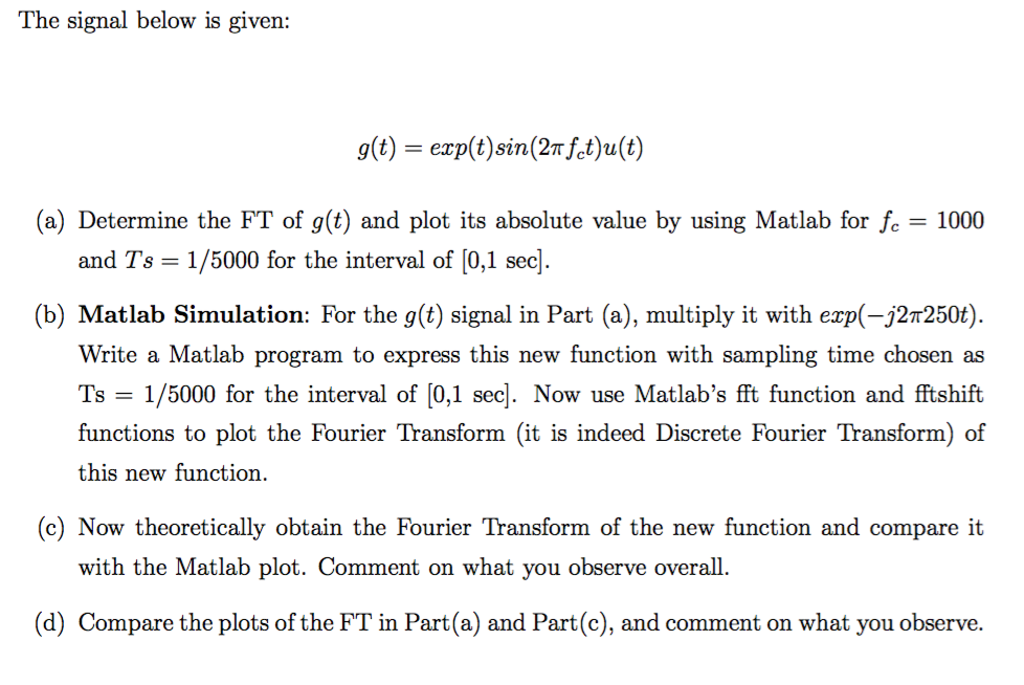
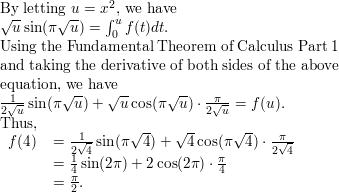How does the term sin (2*pi*f*t) come from? I know that sin and cosine take radians as arguments which will be (pi/2) * (no. of degrees) but why do we mulitply f*t?

SOLVED: Using separation of variables method to solve the IBVP Utt = Uxx; 0 <x<1 t>0 u(o,t)=0=u(1,t) u(x, 0) = 2 sin (Tx) 4(x, 0) = sin (2tx) produces the general solution

B. Current-voltage characteristics of full resistance switching cycles... | Download Scientific Diagram
How does the term sin (2*pi*f*t) come from? I know that sin and cosine take radians as arguments which will be (pi/2) * (no. of degrees) but why do we mulitply f*t?

A transverse wave is described by the equation y = y0sin2pi ( ft - xt ) . The maximum velocity of the particle is equal to four times the wave velocity, if

Using numerical analysis of ordinary differential equation systems to predict the chemical concentration after plasma irradiation: AIP Advances: Vol 12, No 5




![Find the absolute maximum and minimum value of f on [0, pi/2]. F(t) = 2 cos t + sin 2t - YouTube Find the absolute maximum and minimum value of f on [0, pi/2]. F(t) = 2 cos t + sin 2t - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/gjDlr4Igtww/maxresdefault.jpg)

![The set of values of x in [ 0,2π] for which fx=√sin x+cos x is defined is The set of values of x in [ 0,2π] for which fx=√sin x+cos x is defined is](https://df0b18phdhzpx.cloudfront.net/ckeditor_assets/pictures/1418755/original_sinx.png)